
- #Loopback interfaces how to#
- #Loopback interfaces serial#
- #Loopback interfaces drivers#
- #Loopback interfaces update#
For information, see About Anycast Addressing for DNS.
For information, see Configuring IP Addresses on the Loopback Interface.
#Loopback interfaces update#
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set

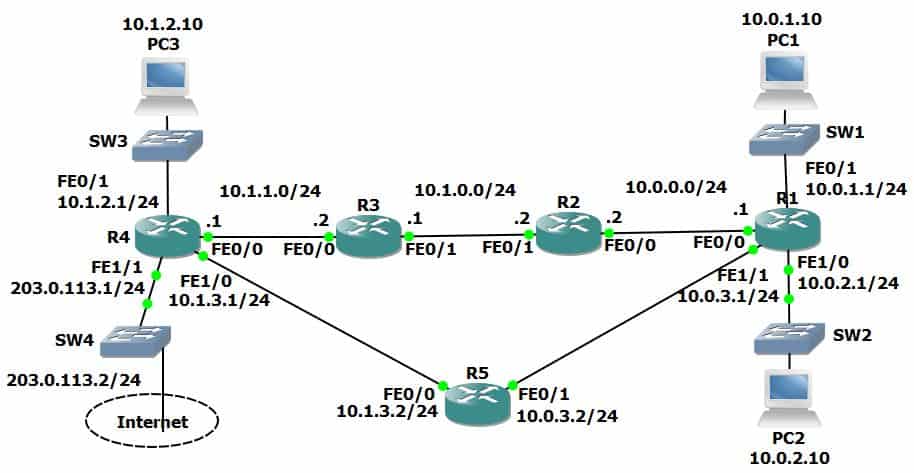
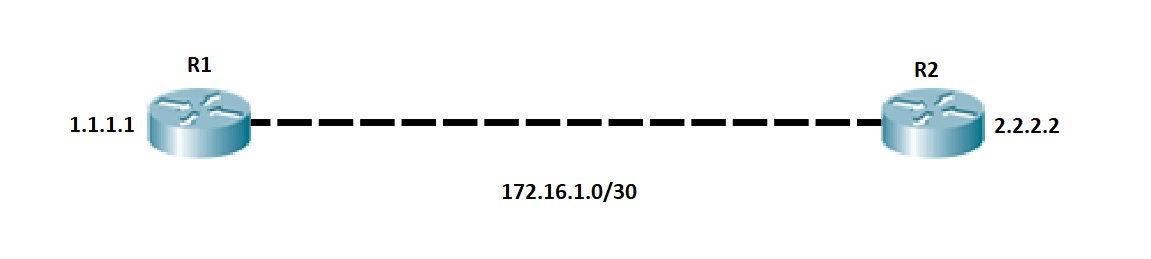
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set Invalid after 0 seconds, hold down 0, flushed after 0 If there is no OSPF Router ID configured, the highest loopback IP address is selected as the OSPF Router ID. Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 2/2/3 ms Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 2/3/4 ms Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2.2.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds: Let’s ping the loopback IP address from both R1 and R2. We can now see that the OSPF neighborship is established. Let’s start by configuring the physical and loopback interfaces. We’ll use the network topology below for the sample configuration.
#Loopback interfaces how to#
I am going to show you how to configure the loopback interface and loopback address and use it as the Router ID for OSPF.
#Loopback interfaces drivers#
#Loopback interfaces serial#
The ‘ip unnumbered’ configuration command allows you to enable IP processing on a serial interface without assigning it an explicit IP address.

You can also configure the loopback address as the Router ID for routing protocols like OSPF and BGP.A good example is mapping a router’s loopback IP address to its DNS server address.We would reap the following advantages and benefits of having loopback interfaces and loopback addresses in our network: Loopback addresses are not limited to the 127.0.0.0/8 block.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
